System
Click the System menu item to expose additional pages
Time Settings -
See Time settings
Hardware Activation
EVO’s expansion hardware (including all drives and added Ethernet) must be activated to work properly in the EVO environment. This guarantees that the hardware used is the tested and approved hardware for the EVO system. All EVO base units are authorized to activate the first two drive quads by default. Additional hardware is activated using an Activation code provided by SNS.
Once activations are authorized, this page is used to activate the expansion hardware.
Warning
The addition of any expansion hardware to EVO requires prior authorization from SNS.
Expansion quad licensing
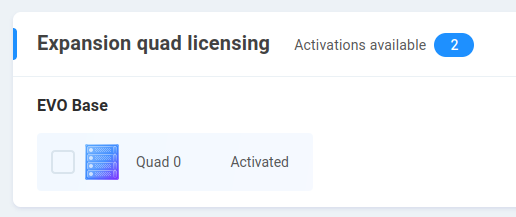
EVO includes authorization for two quads by default. Additional quads may be authorized for expansion and activated at this page.
Warning
Deactivating a quad is a destructive operation. Only deactivate a quad if the intent is for EVO to treat the disks as unformatted drives needing to be activated.
Deactivate missing quads
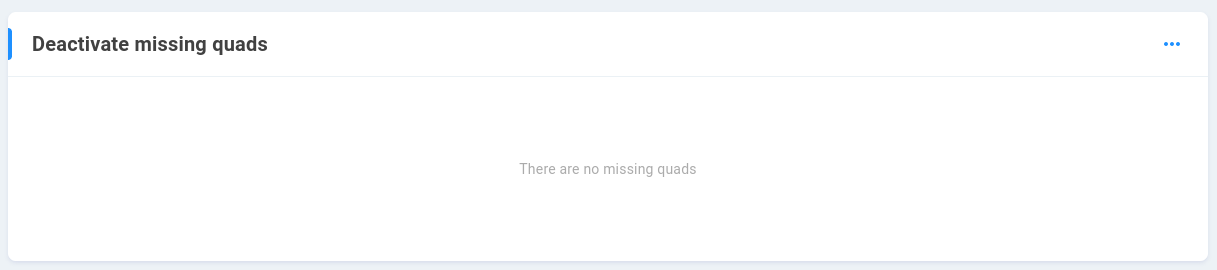
Hardware changes, such as moving disks between EVOs, may lead to a situation where EVO finds information about quads that is not part of its current configuration, or is expecting to find quad information that is not present on the installed data drives. Only deactivate any quads listed in this section if the current EVO configuration is known to be good and extraneous information is to be removed.
Warning
Once deactivated, any missing quads cannot be reactivated.
Ethernet expansion connectivity licensing
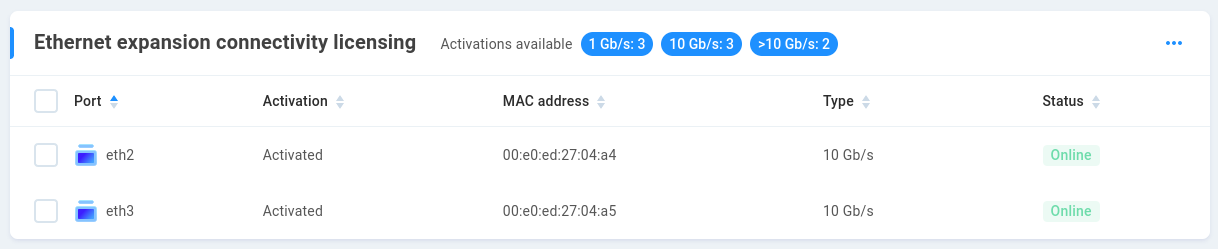
Any network hardware changes will need to be authorized and activated (or deactivated if removed). Each network port on an adapter is treated as a device according to its MAC address, and may be activated/deactivated in this section.
Add activation keys
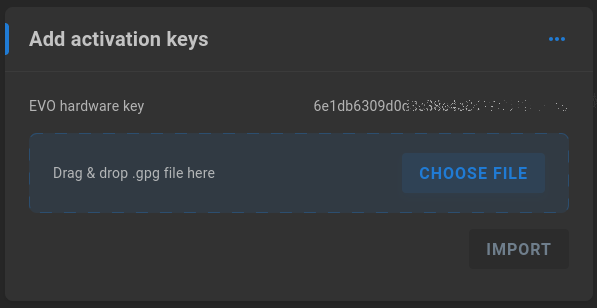
The EVO hardware key is displayed, and additional activation keys provided by SNS may be uploaded. Drag and drop the key or click “CHOOSE FILE” to browse and locate the key for upload.
Network -
See Network
Disks & Pools -
See Disks & Pools
Logical Disks -
See Logical Disks
Pools -
See Pools
Advanced
Ethernet bonding parameters
Ethernet bonding is typically referred to as link aggregation, and the default values in EVO are expected for most environments, with LACP being the most common aggregation method enabled on network switches.
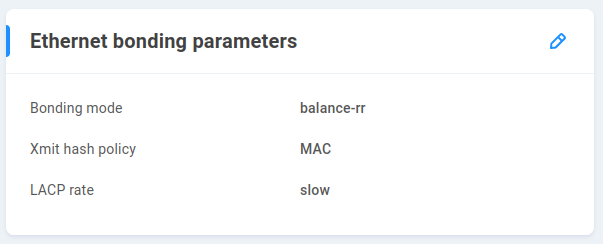
Bonding mode - 802.3ad (LACP) is the default. Some environments may have a need to set up a different aggregation protocol, and choices available are balance-rr, active-backup, balance-xor, broadcast, balance-tlb, and balance-alb. The implications for each mode are outside the scope of this document.
Xmit hash policy - For 802.3ad mode, the Xmit Hash Policy controls the distribution of client workstations across EVO’s bonded ports. The Xmit Hash Policy can be set to MAC (layer-2) or MAC+IP (layer-2-and-3). Both policies are compliant with the 802.3ad specification.
LACP rate - This value is the rate at which LACP packets are sent. In the default mode, LACP PDUs are sent each second until the devices synchronize, after which they’re sent every 30 seconds. When LACP fast is set, PDUs are still sent every second following synchronization. There are pros and cons to each approach, since a timeout may not be immediately corrected using the slow rate, while the fast rate will add mostly unneeded network traffic, and may not handle a timeout with any significant difference. Most switches use the same default, so this value should only be changed to match a switch using fast rate.
Note
The LACP rate does not directly translate to communication speed (slow may in fact be good).
NAS Recycle Bin
A recycle bin is included and enabled by default for local EVO SMB shares. By default, files are permanently deleted after one week in the recycle bin.
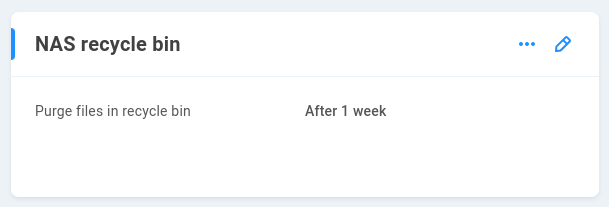
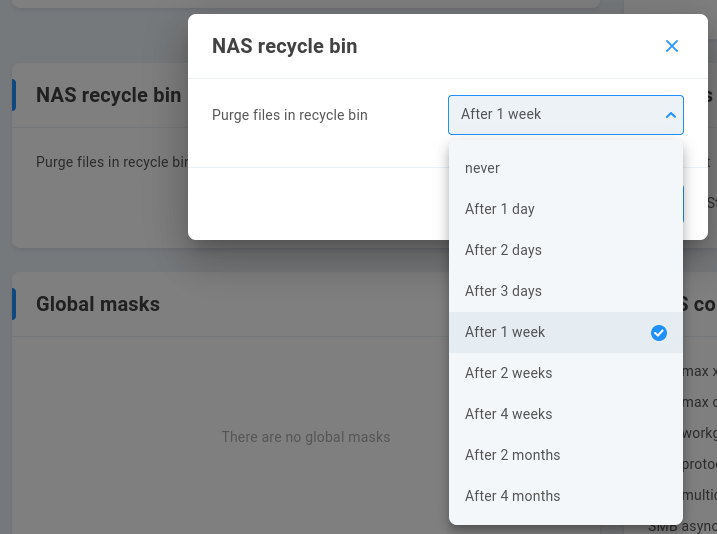
The retention time for SMB user-deleted content can be selected from the drop-down menu after clicking the pencil to edit.
Warning
The recycle functionality applies to content deleted over SMB. Other methods of modifying content (Slingshot, other protocols) will not use SMB, and will therefore not send content to the recycle bin.
Graphs
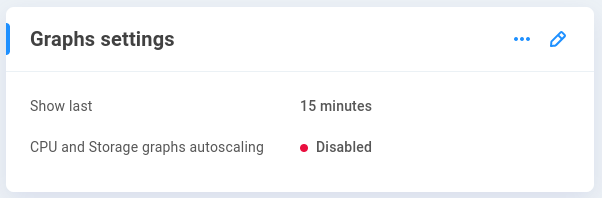
This provides options for the reporting of system statistics in the collapsible display at the top of the interface.
Click the pencil to edit the settings:
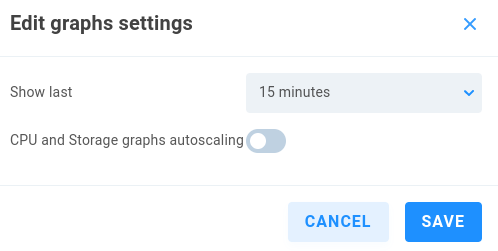
Show last - 15 minutes (default), 30 minutes, 1 hour
CPU and Storage graphs autoscaling - Toggles automatic scaling to fit default display values (off by default)
Global Masks
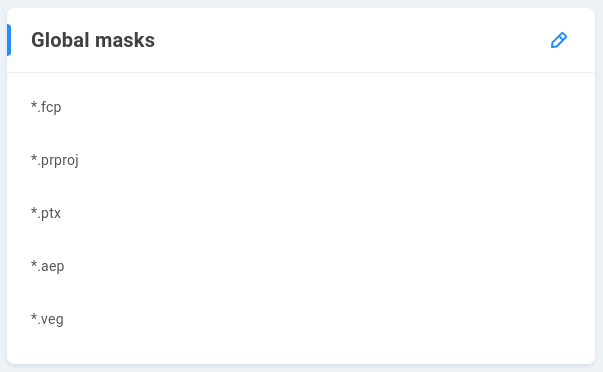
If Project locking is enabled for any NAS share(s), EVO will automatically lock the file types in this list when accessed via read/write by an SMB user. The most common file types where this behavior may be expected are enabled by default, and it’s possible to add or remove file extensions for custom locking behavior.
NAS Configuration
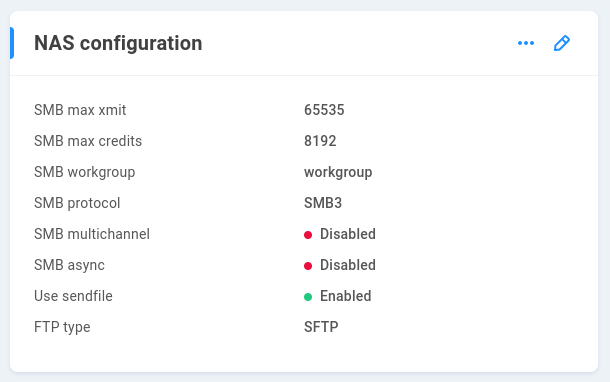
SMB max xmit - This sets the maximum transmit size for SMB requests accepted by the server (determined by client). The default value is 65535 (maximum allowed).
SMB max credits - Credits determine the amount of simultaneously allowed client requests. The default value is 65535 (maximum allowed).
SMB workgroup - This is a peer-to-peer local network for SMB-connected machines. By default, the workgroup name will be WORKGROUP, which should update automatically if needed, for example by joining Active Directory.
SMB protocol - SMB3 is used by default, with the option to lower to SMB2 if required by legacy clients.
SMB multichannel - Disabled by default. When configured, SMB multichannel allows a client to use more than one NIC to communicate with the server. This should only be enabled if the network and clients have been configured to support it.
SMB async - Disabled by default. SMB async can increase the number of concurrent file operations, though EVO uses the sendfile feature instead of SMB-specific asynchronous I/O. This setting should be enabled if SMB multichannel is enabled. It may not be enabled if sendfile is enabled.
Use sendfile - Enabled by default. This allows for more efficient calls to the file system for oplocked files. Disable in order to use SMB multichannel with SMB async.
FTP type - If a share is created with FTP access, it will allow SFTP connections only by default. This may be changed to FTP or FXP if needed.
SMB encryption - Disabled by default. Optionally enable encryption for SMB traffic. Note that this setting applies to all EVO-local SMB shares and that the added security may impact workstation performance when working with SMB shares.
Use catia+fruit - Enabled by default, and required by some applications, such as Final Cut Pro for macOS. These modules are intended to improve handling for some special characters allowed by macOS and unsupported over SMB, which may be beneficial in a cross-platform environment (Windows and Mac). If Mac workstations are used, take care when toggling the setting if data is already in place, especially if files contain special characters other than dots, dashes, and underscores.
Use server-side copy for macOS - Disabled by default. Enabling may improve operation speed for file transfers initiated by a workstation from one EVO share to another EVO share. Note that Finder may not show the same incremental progress when server-side copying is enabled.
Cluster
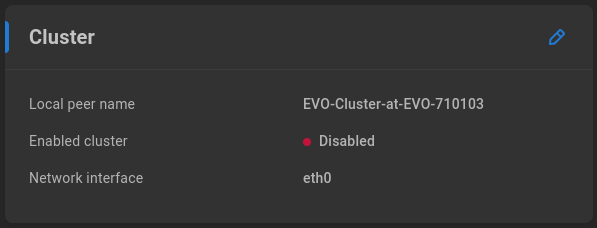
If the capacity requirements exceed what’s offered simply by adding expansion chassis to a head unit, it’s possible to configure multiple head units together as a cluster, providing a single gateway address to be used for a large Nearline storage array. Clustered systems are typically preconfigured by SNS. Consult with the account manager and/or SNS support before attempting to repurpose existing hardware.
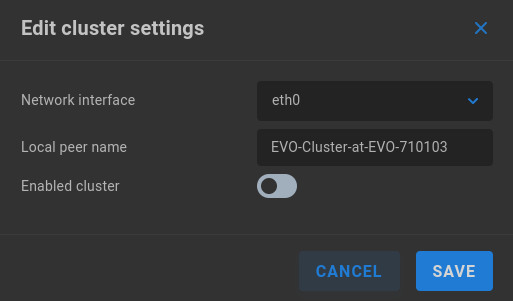
Network interface - Select Ethernet port to be used for cluster backbone communication
Local peer name - Prepopulated according to host name, and may be edited prior to configuring cluster.
Enabled cluster - Disabled by default. Enable to incorporate EVO as a cluster node.
TCP Scaling
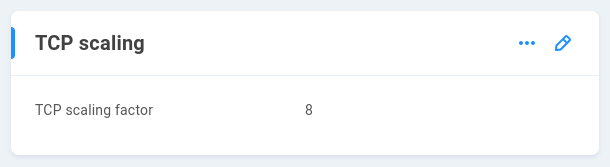
TCP scaling factor - Default scaling factor is 8, and may be set to any value between 4 and 14.
TCP window scaling is already enabled on any modern operating system, and workstations and EVO will continually negotiate in an attempt to determine the largest window size they can reliably use for communication, based on ever-changing network variables. Adjusting the scaling factor may result in improved or worsened communication and resource usage. The default value is well-balanced and generally sufficient for most environments.
Power & UPS
This system is designed to remain “up” and online for very long durations. In fact, leaving it up and running is preferable to shutting it down very frequently. If everything is working normally but you prefer to routinely reboot, then a schedule of approximately every 12-24 weeks is more than sufficient.
One short push of the front panel Power button will also initiate the shutdown process, which normally takes a few minutes. If you have an expansion chassis, it is designed to remain powered on even when the main unit has been powered down.
Note
Ensure all EVO and expansion chassis share a single common conditioned source of power.
Power
This section provides reboot and shutdown options. Shutdown can also be initiated with a tap of the power button on the chassis.
APC UPS configuration -
Hardware Profile
The Hardware Profile page identifies and provides statistics for internal components. Output may differ based on EVO model.
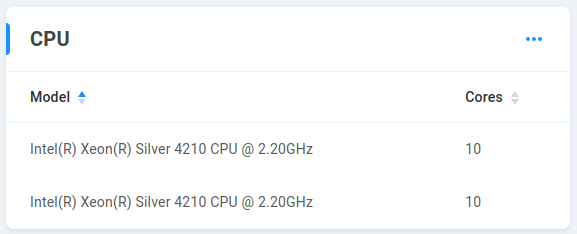
CPU - Displays CPU type and core total
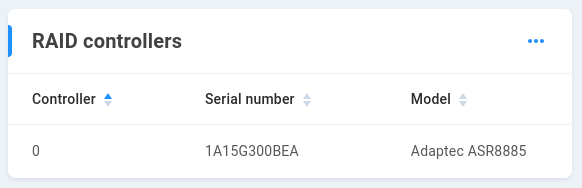
RAID controllers - Shows disk controller(s), serial and model numbers. The first controller is enumerated 0.
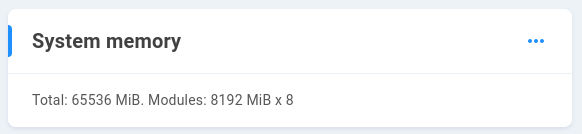
System memory - Shows total system memory, size and number of modules installed
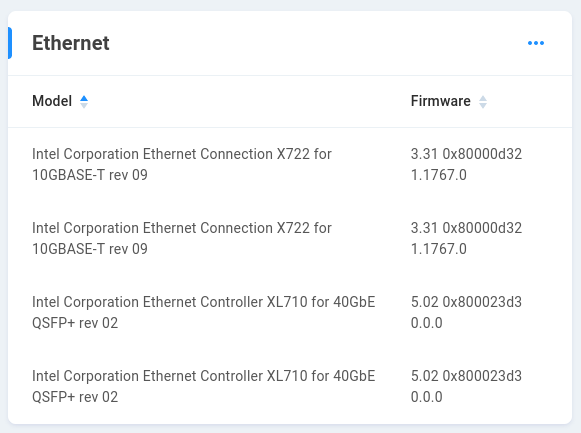
Ethernet - Displays model and firmware information for onboard and any added Ethernet expansion hardware
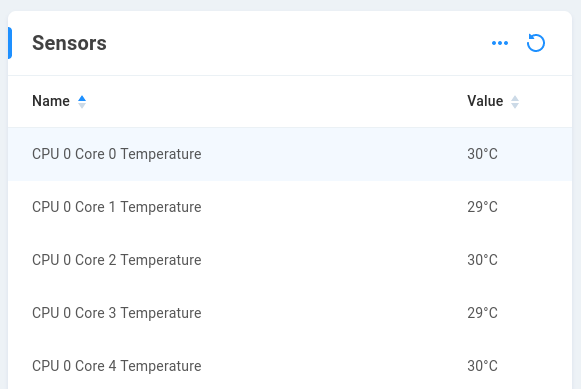
Sensors - Individual CPU core temperatures are displayed, as well as a combined temperature value for the CPU.
Admin Settings
Networking settings
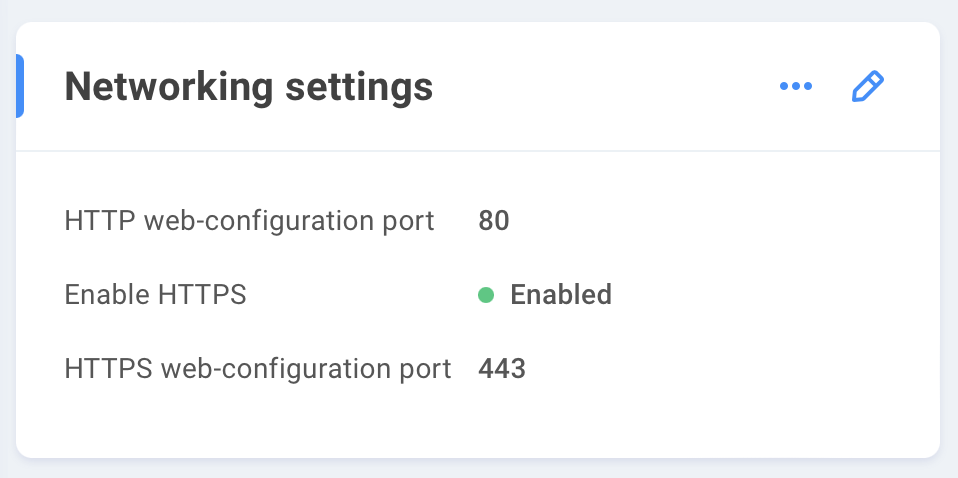
HTTP web-configuration port - 80 is the default and standard port for http communication. Manually changing this port will impact any applications that expect to use port 80.
Enable HTTPS is disabled by default and requires additional configuration to enable. See Server certificate below
HTTPS web-configuration port - 443 is the default and standard port for https communication. Manually changing this port will impact any applications that expect to use port 443.
Warning
Do not enable HTTPS until prepared to do so with the required certificate. Workstations will require additional configuration in order to reach EVO once HTTPS is enabled.
Primary administrator
Current login - EVO administrator name is masked
Current password - EVO administrator password is masked
Click the pencil to edit the primary administrator credentials.
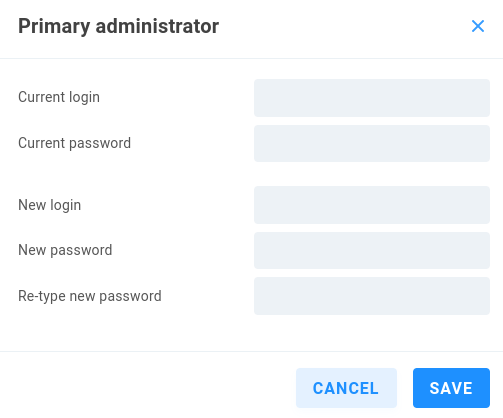
Current login - Enter the current primary EVO administrator name (admin)
Current password - Enter the current primary EVO administrator password (adminpw111)
New login - Enter the new primary EVO administrator name
New password - Enter the new primary EVO administrator password
Re-type new password - Confirm the new primary EVO administrator password
Server certificate
A server certificate needs to be uploaded to EVO in order to enable https communication between EVO and workstations. Configuring secure web communication requires server and client validate each other by means of a certificate of trust. The certificate can be self-signed or granted by a certificate authority.
Click the three dots to choose to add the card to the Home page, create a new certificate, or import/export an existing certificate.
Create certificate
Adding a certificate allows for establishment of secure channels using HTTPS between server and users, whereby they’re able to safely determine the computer they’re communicating with is in fact the one it claims to be.
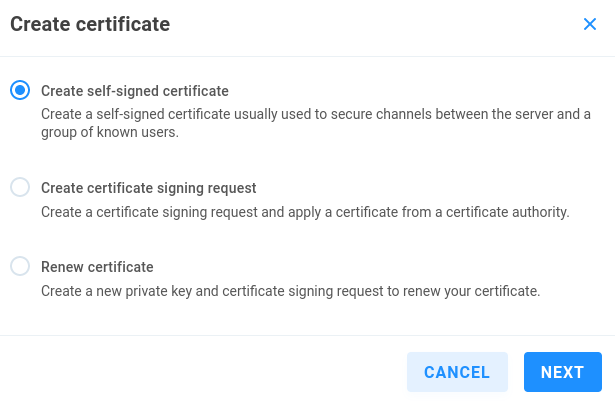
Create self-signed certificate - This allows for any user to create and sign a certificate, as a certificate authority. In addition to adding the signed certificate to EVO, client machines must be configured to explicitly trust the self-signed certificate.
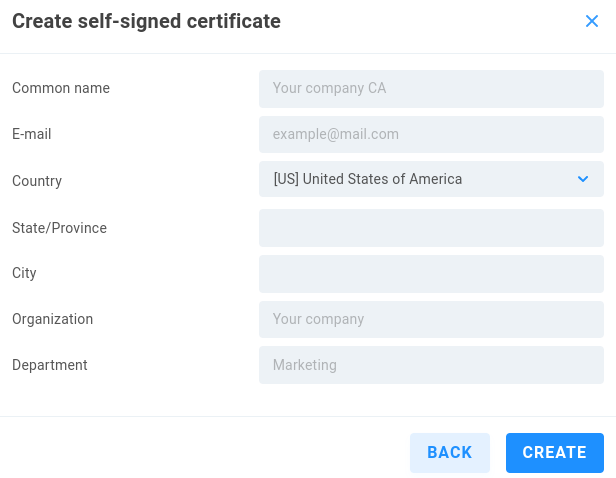
The values entered here are rather arbitrary, as the certificate is manually validated by clients.
Common name - Enter a name to act as the certificate authority
E-mail - Enter an email address to associate with the authority
Country - Select country
State/Province - Enter state or province if applicable
City - Enter city
Organization - Enter a name for reference
Department - Enter a name for reference
Create certificate signing request - Create a certificate signing request to use for certificate signing by a certificate authority.
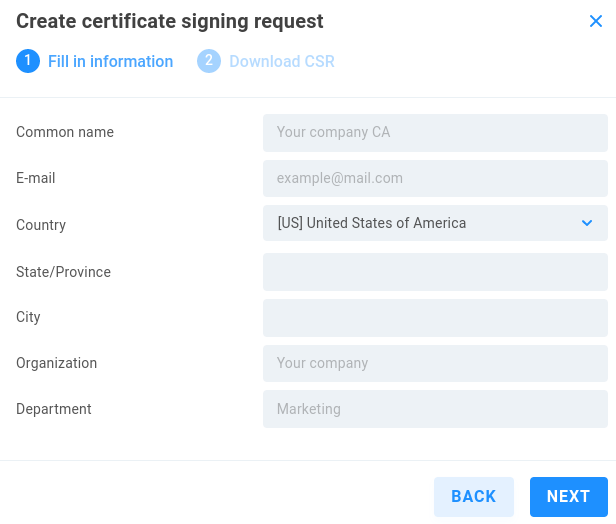
The values entered here are required for review by the certificate authority.
Common name - Enter a name to associate with the certificate
E-mail - Enter an email address to associate with the certificate
Country - Select country
State/Province - Enter state or province if applicable
City - Enter city
Organization - Enter a name for reference
Department - Enter a name for reference
Click NEXT, then Click DOWNLOAD to export your certificate signing request. Send this certificate signing request to a third-party certificate authority for their signing. Once your certificate has been issued, choose Import certificate from the Server certificate card.
Renew certificate - Create a new private key and certificate signing request to renew your certificate.
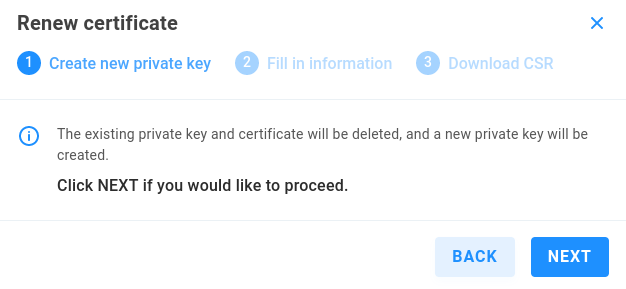
The existing private key and certificate will be deleted, and a new private key will be created. Click NEXT if you would like to proceed.
Fill in information as described in Create certificate signing request.
Download CSR
Once a certificate is in place, https can be enabled at Networking settings.
Warning
Since a self-signed certificate is not provided by a trusted certificate authority, client workstations have no means for automatic trust verification and will need an exclusion added for trusting the self-signed certificate.
Import certificate
Import signed CSR - Use this to import a signed certificate following EVO creation of a certificate signing request.
Import certificate - This option allows for import of an existing certificate and private key.
Warning
Until a certificate is in place, HTTP will be used for upload, so ensure your connection is isolated.
Drag & drop the file or click Choose File and browse to upload a signed certificate
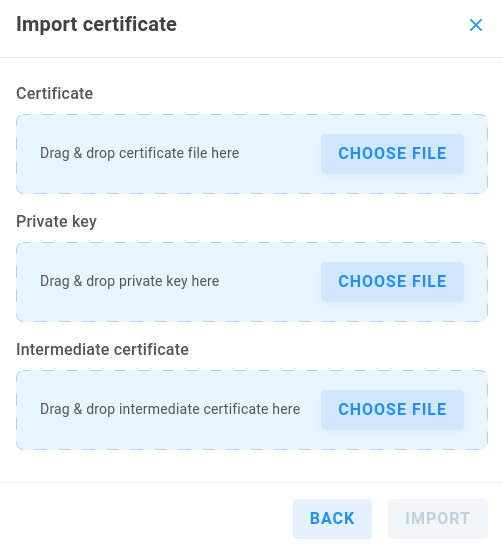
Drag & drop the files or click Choose File and browse to upload each. The certificate format may be .pem or .crt, and the key may be .pem or .key format.
Export certificate
Click Export certificate to download EVO’s server certificate (evo-web.crt) for import to another device’s trusted certificates (such as macOS Keychain or Windows Trusted Root Certification Authorities).
Restrict EVO UI access
By default, EVO’s administrative interface is available via any of its Ethernet ports, or any device with a network path to EVO. It’s additionally possible to restrict administrative access to a single Ethernet port, which may be isolated from the rest of the local network.
Restrict EVO UI access - Disabled by default. Enable to restrict interface access to a single Ethernet port.
Allowed interface - Choose the Ethernet port you’d like to reserve for administrative access.
Secondary administrators
While the Primary EVO administrator has access to all interface functionality, it may be useful to protect these credentials and create one or more secondary administrators with limited additional permissions for common administrative tasks, such as the ability to create a new share, without permission to delete one.
Click the pencil to manage the list of secondary administrators.
Add an administrator - Enter or choose a name from the list.
Display language
EVO offers localization options. Select English or Simplified Chinese from the drop-down menu to change the interface language. Contact SNS if you’re interested in adding support for another language.
Long-lived tokens
If multiple EVOs are configured (federated), long-lived tokens can assist with automatic reconnection in the event of interrupted communication (reboot, for example). If a token expires, federation may require reconfiguration.
Click the pencil to expose additional actions for long-lived tokens.
Revoke all tokens - Removes all active long-lived tokens. Federated EVOs will be disconnected from federation.
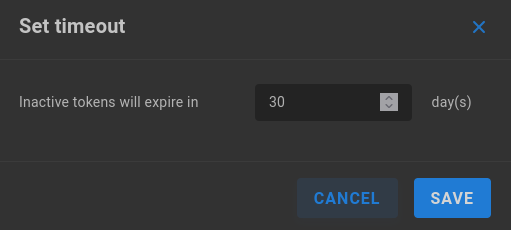
Set timeout - Long-lived tokens expire after 30 days by default. The max value is 365 days.
See EVO Federation for more information.
Firewall
Firewall rules may be added directly to EVO to restrict port access by client IP according to inclusion and/or exclusion rules. Logic for multiple rules and policies can be implemented by changing the order in which the rules are applied.
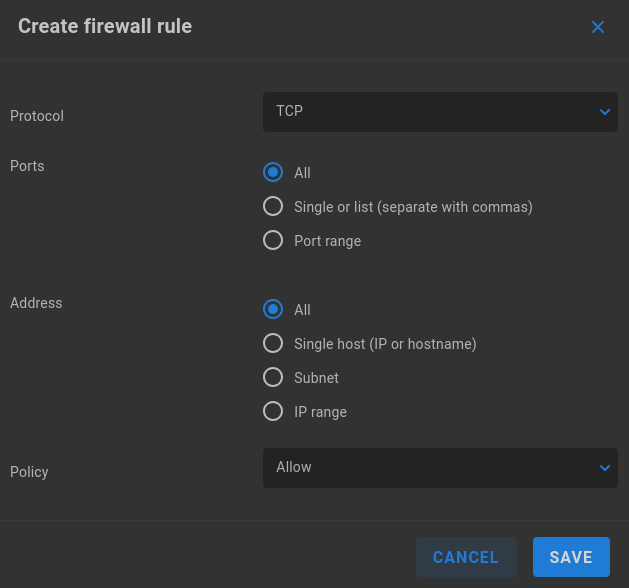
Protocol - Select TCP or UDP. Some communication methods expect both transport types, requiring an additional rule.
Ports - Select All, specify a port or comma-separated list of ports, or define a port range
Address - Select All to apply to all client IP addresses, single host by IP or hostname, or define a subnet using CIDR notation
Policy - Select Allow or Deny to specify whether packets that meet the defined conditions should be accepted or dropped.
Warning
It is possible to inadvertently add a rule that blocks all access to the interface. As a protection, saving an added rule applies it for five minutes, after which changes will be automatically rolled back. This allows for rules to be fully tested before committing them. Once functionality for the added rule(s) is confirmed, click commit to apply the rule set.
User Auditing
SMB User Auditing may be enabled to track actions taken by users on the file system. When configured, details about user read and write operations, including modification and deletion, are available for review.
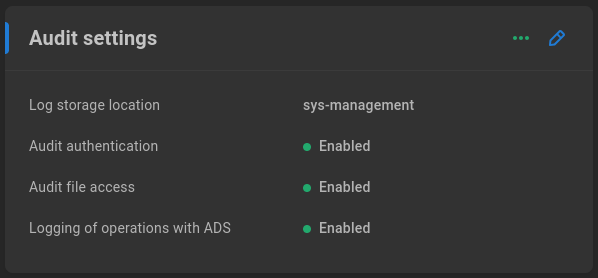
Audit settings
Click the pencil to edit audit settings.
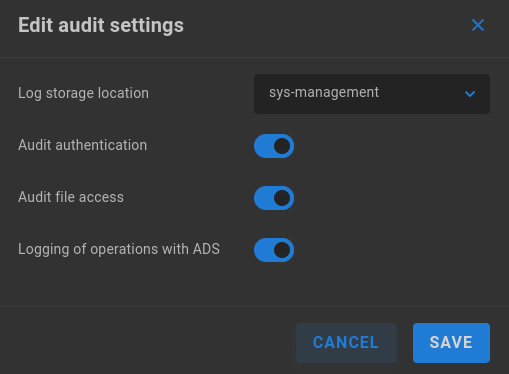
Log storage location - Select a share from the dropdown menu to store audit logs.
Audit authentication - When enabled, SMB user authentications are logged.
Audit file access - When enabled, SMB user file operations (reads, writes) are logged.
Logging of operations with ADS - When enabled, Active Directory operations are logged.
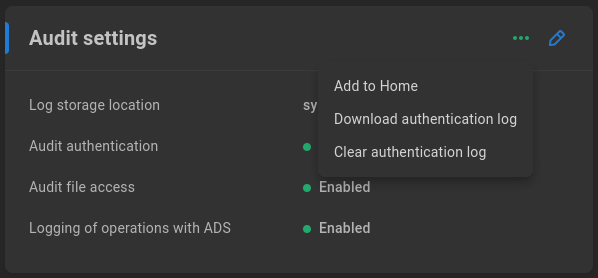
Click the three dots to download or clear the authentication (SMB user login) log.
Auditing notice
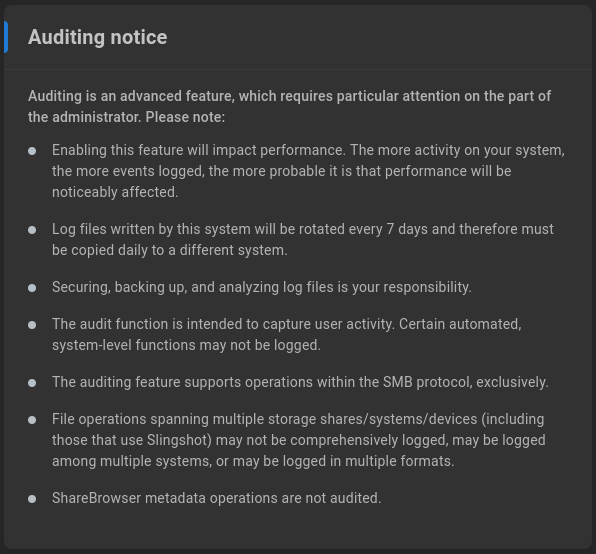
Auditing is an advanced feature, which requires particular attention on the part of the administrator. Please note:
Enabling this feature will impact performance. The more activity on your system, the more events logged, the more probable it is that performance will be noticeably affected.
Log files written by this system will be rotated every 7 days and therefore must be copied daily to a different system.
Securing, backing up, and analyzing log files is your responsibility.
The audit function is intended to capture user activity. Certain automated, system-level functions may not be logged.
The auditing feature supports operations within the SMB protocol, exclusively.
File operations spanning multiple storage shares/systems/devices (including those that use Slingshot) may not be comprehensively logged, may be logged among multiple systems, or may be logged in multiple formats.
ShareBrowser metadata operations are not audited.
Note
User Auditing is available for the SMB protocol exclusively. File modifications by other means are not tracked by the User Auditing feature.
Audit Filter
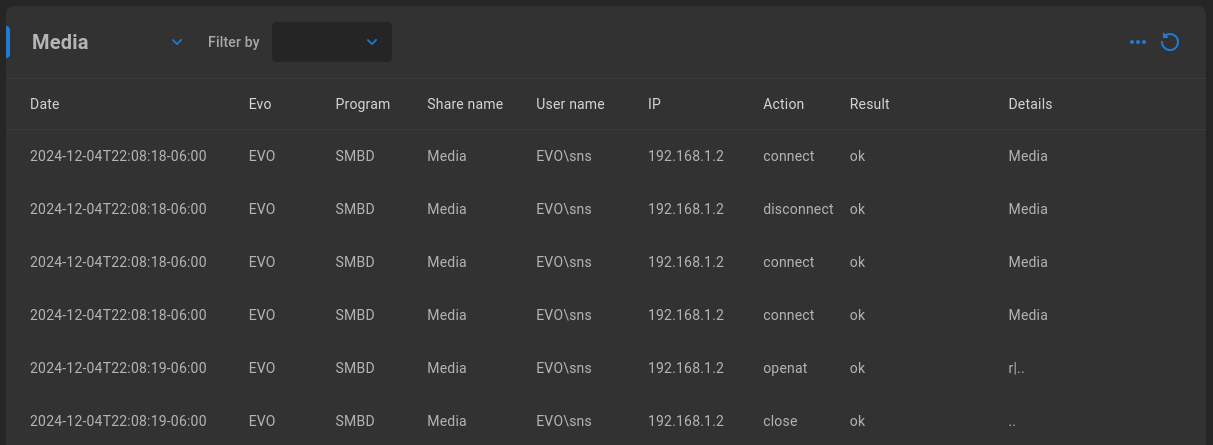
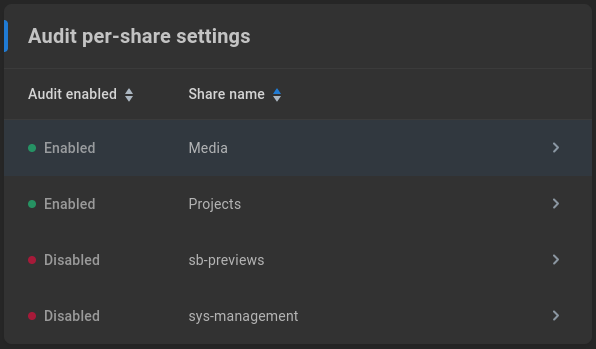
In addition to the log stored at the setting specified in Audit settings and the download available in Audit per-share settings <Audit per-share settings, a live audit filter is available for administrator review. Select the share to review from the first dropdown menu, and optionally filter by user name, IP, date, file name, or actions (default shows all).
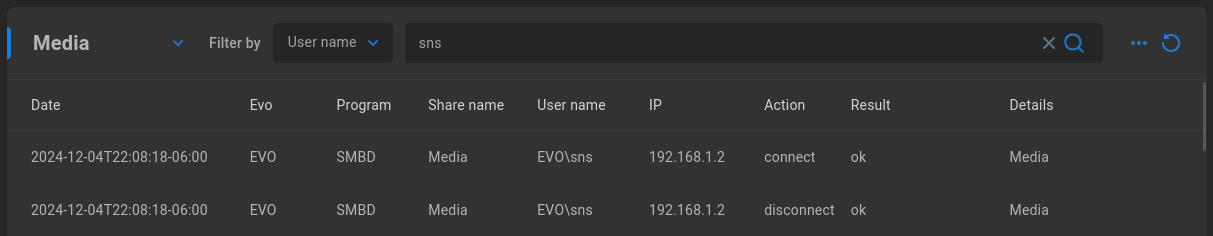
Once a filter is selected, a search box appears. Enter a search term to further filter the results.
Cloud VPN -
See Cloud VPN.